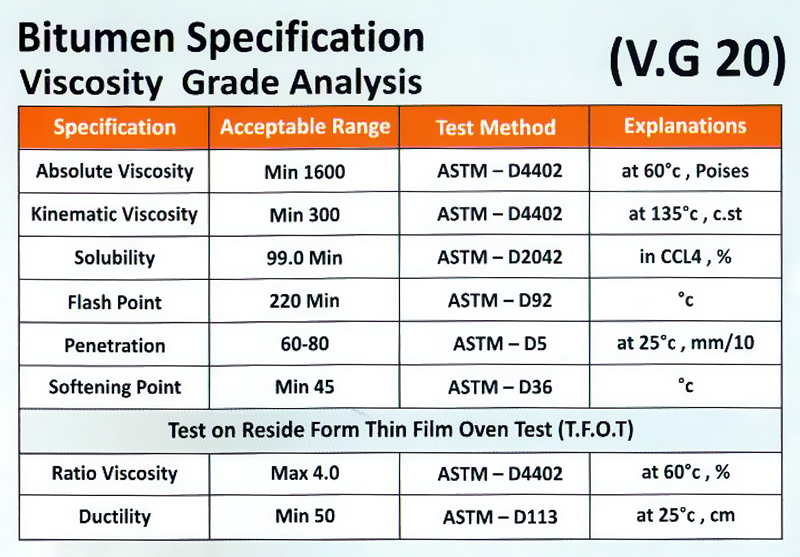
VG 20
Viscosity is a key property of Bitumen that is closely related to its consistency and flowability. Viscosity refers to the resistance of a fluid to flow or deformation under an applied force. In the context of Bitumen, viscosity is a measure of its resistance to flow at a particular temperature and shear rate.
Viscosity is an important characteristic of Bitumen because it determines its ability to be pumped, mixed, and applied in various industrial applications, including road construction, waterproofing, and roofing. The viscosity of Bitumen is strongly dependent on temperature, with higher temperatures generally resulting in lower viscosity values.
Bitumen viscosity is typically measured using a viscometer, which applies a specific shear rate to the Bitumen sample and measures the resulting resistance to flow. There are several methods for measuring Bitumen viscosity, including the Brookfield viscometer, kinematic viscosity, and dynamic viscosity.
Viscosity grading is one of the commonly used methods for classifying Bitumen based on its viscosity at 60°C. In this system, Bitumen is classified into different viscosity grades, ranging from AC 2.5 to AC 30, with lower viscosity grades indicating more fluid or flowable Bitumen.
To make long story short, viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow or deformation under an applied force. In the context of Bitumen, viscosity is an essential property that determines its ability to be pumped, mixed, and applied in various industrial applications. Bitumen viscosity is measured using a viscometer and is strongly dependent on temperature. Viscosity grading is a commonly used system for classifying Bitumen based on its viscosity at 60°C.